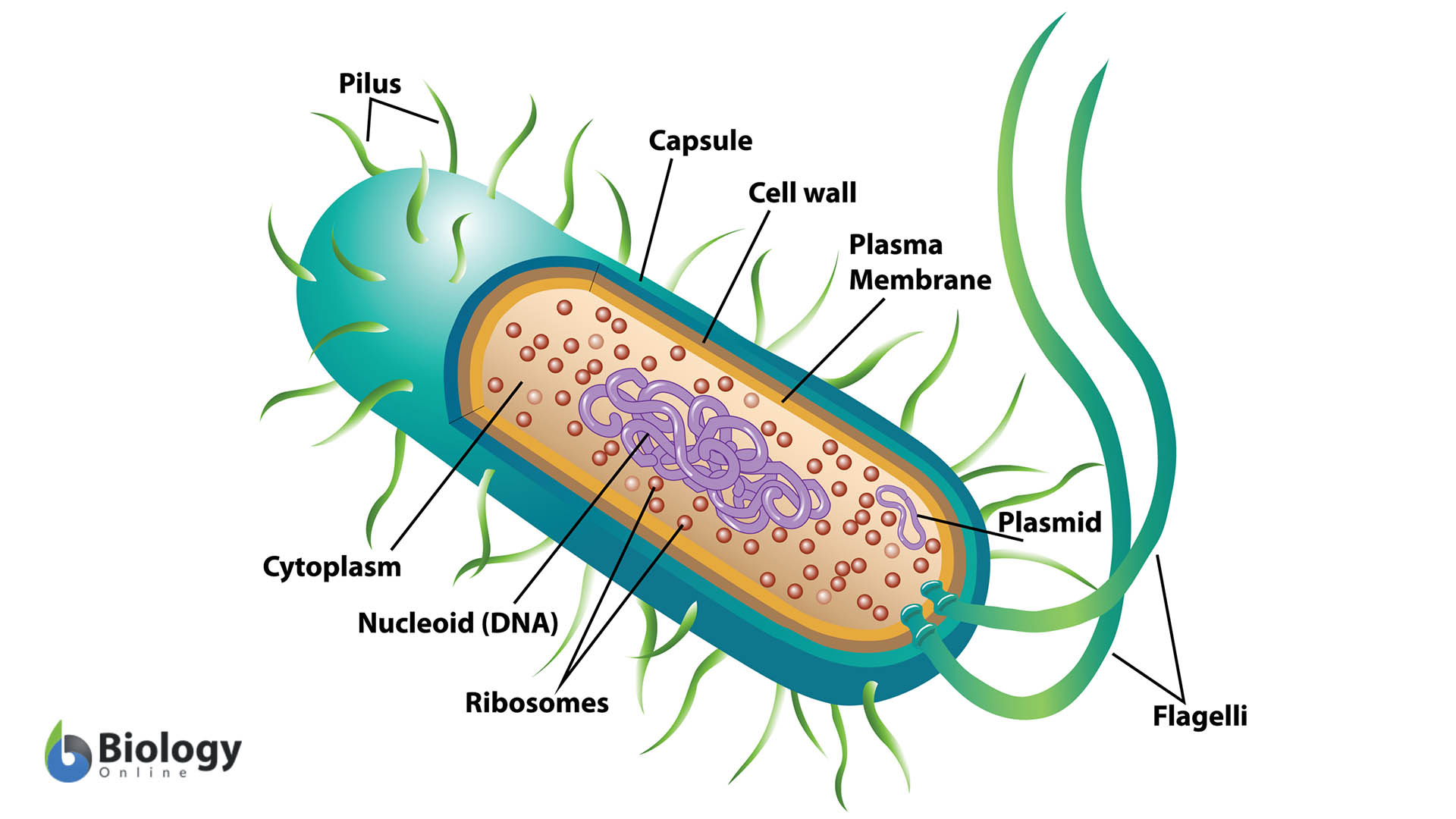
 Eubacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms consisting of a single cell lacking a nucleus and containing DNA is a single circular chromosome. Eubacteria can be either gram-negative or gram-positive, they have economic, agricultural, and medical importance.
Eubacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms consisting of a single cell lacking a nucleus and containing DNA is a single circular chromosome. Eubacteria can be either gram-negative or gram-positive, they have economic, agricultural, and medical importance.